Bolted fault current calculation is a fundamental part of IEEE 1584 guidelines for arc flash analysis. Here’s how it’s calculated and the effect of ground resistance:
How is the Bolted Fault Current Calculation in IEEE 1584-2018 Done?
Bolted fault current is the theoretical current that would flow in the event of a direct (zero-impedance) short circuit, such as if conductors were clamped together without any impedance between them. It’s calculated based on several parameters of the electrical system, including:
- System Voltage: The voltage level of the equipment or part of the system where the fault is assumed to occur.
- Impedance of the Power System: This includes the impedance of the transformer, cables, and any other devices within the fault loop that may limit the current.
- Transformer Characteristics: Including kVA rating, impedance percentage, and primary and secondary voltage.
IEEE 1584 primarily focuses on the bolted fault current because it’s the foundation for determining incident energy and arc flash boundary in a system.
Role of Ground Resistance per IEEE 1584 – 2018
Ground resistance does not play a significant role in the calculation of bolted fault current. Since bolted faults are assumed to have negligible impedance, the current is not influenced by the resistance in the ground path. However, ground resistance may impact other types of faults, such as line-to-ground faults, where impedance in the ground path could affect fault current levels and distribution.
For arc flash studies, IEEE 1584 – 2018 assumes a worst-case bolted fault condition (typically three-phase faults), which simplifies calculations by ignoring the effect of ground resistance, providing conservative estimates for safety.
Definitions Screen Shot from the Standard:
available short-circuit current: At a given point in a circuit, the maximum current that the power system can deliver through a given circuit to any negligible-impedance short circuit applied at the given point, or at any other point that causes the highest current to flow through the given point. “Available short-circuit current” and “bolted fault current” are equivalent for a zero fault impedance.
bolted fault: A short-circuit condition that assumes zero impedance exists at the point of the fault.
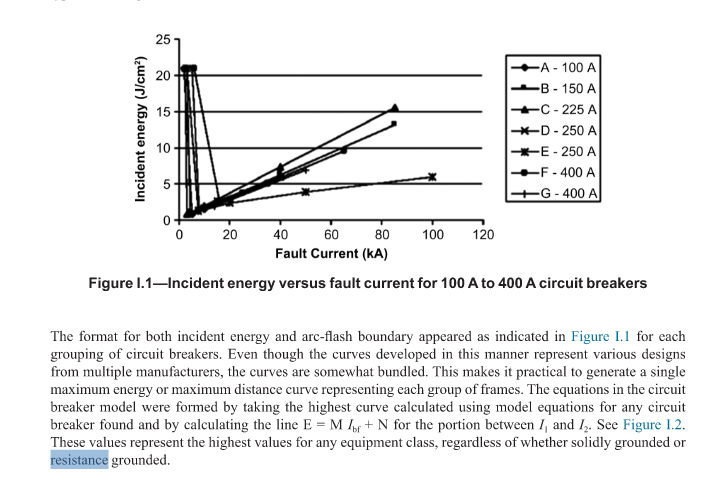
Case of Resistance and calculations from the Study
Understanding bolted fault current is essential for accurate arc flash analysis and electrical safety planning. By following IEEE 1584-2018 guidelines, you can ensure safer work environments and compliance with industry standards. For any electrical system, calculating the bolted fault current provides a foundation to evaluate potential incident energy levels and establish necessary arc flash boundaries. Ready to enhance the safety and compliance of your operations? Contact Us today to get expert support on bolted fault current calculations, arc flash studies, and comprehensive electrical safety assessments.