Understanding Arc Flash Risk Assessments: OSHA’s Essential Mandate for Workplace Safety
In the realm of workplace safety, few hazards are as potentially catastrophic as an arc flash event. These sudden releases of electrical energy can result in intense heat, blinding light, deafening sound, and deadly shrapnel flying at high speeds. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) recognizes the gravity of arc flash incidents and has mandated arc flash risk assessments to mitigate these dangers.
What is an Arc Flash Risk Assessment?
An arc flash risk assessment is a comprehensive evaluation of potential arc flash hazards in the workplace. It involves identifying areas where arc flashes may occur, assessing the severity of potential incidents, and implementing safety measures to minimize risks to personnel and equipment.
Why Are Arc Flash Risk Assessments Necessary?
Arc flash incidents pose significant risks to both personnel and property. Employees working on or near energized electrical equipment are particularly vulnerable. These hazards can result in severe injuries, including burns, blast injuries, and even fatalities. Furthermore, arc flashes can cause extensive damage to electrical systems, leading to costly downtime and repairs.
OSHA requires employers to provide a safe working environment for their employees, including protection against electrical hazards like arc flashes. Failure to comply with OSHA regulations can result in hefty fines and legal repercussions. Therefore, conducting arc flash risk assessments is not just a matter of compliance but also crucial for safeguarding the well-being of workers and the integrity of facilities.
OSHA’s Regulations on Arc Flash Risk Assessments
OSHA’s regulations regarding arc flash risk assessments are outlined in several standards, including:
- 29 CFR 1910 Subpart S – This standard covers electrical safety requirements for general industry workplaces. It mandates that employers assess the workplace for potential electrical hazards, including arc flash risks, and implement appropriate safety measures.
- 29 CFR 1926 Subpart K – Similar to Subpart S, this standard applies to construction workplaces and requires employers to identify and mitigate electrical hazards, including arc flashes.
- NFPA 70E – While not an OSHA regulation, the National Fire Protection Association’s (NFPA) Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace (NFPA 70E) provides guidelines for arc flash risk assessments. OSHA often references NFPA 70E as a recognized industry consensus standard for electrical safety.
Key Components of Arc Flash Risk Assessments
An effective arc flash risk assessment typically includes the following steps:
- Identification of Hazardous Areas: Determine which areas in the workplace pose arc flash risks, such as electrical panels, switchgear, and circuit breakers.
- Analysis of Equipment and Systems: Evaluate the characteristics of electrical equipment and systems to assess the likelihood and potential severity of arc flash incidents.
- Labeling: Properly label electrical equipment with arc flash warning labels, including information such as the incident energy level, arc flash boundary, and required personal protective equipment (PPE).
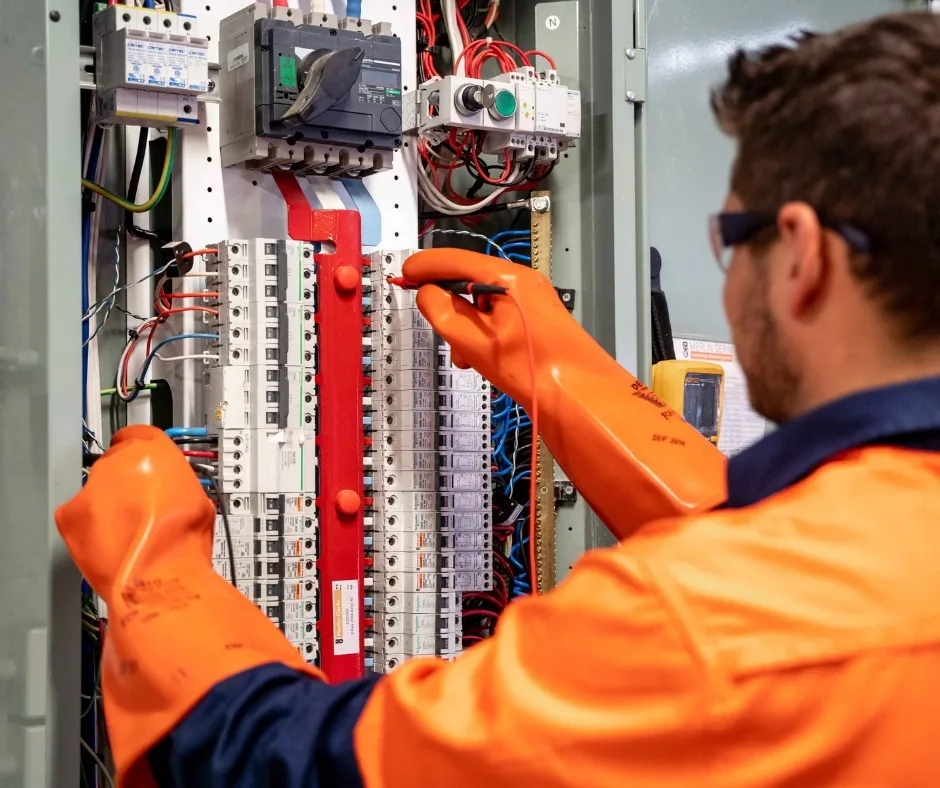
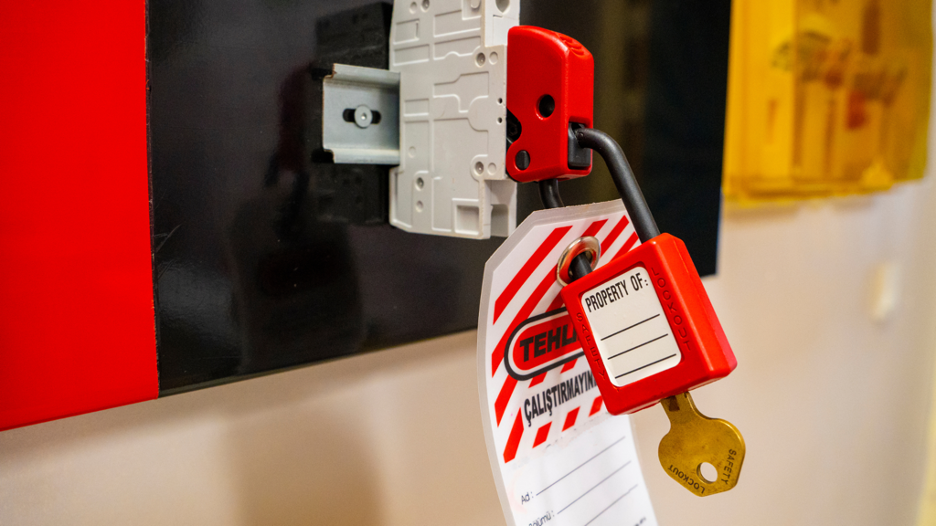
- Establishment of Safety Procedures: Develop and implement safety procedures for working on or near energized equipment, including de-energization protocols, lockout/tagout procedures, and PPE requirements.
- Training and Education: Ensure that employees receive adequate training on arc flash hazards, safety procedures, and the proper use of PPE. Training must occur every 3 years to stay compliant.
In conclusion, an Arc flash risk assessment is an essential component of workplace safety programs, mandated by OSHA to protect employees from the potentially catastrophic consequences of arc flash incidents. By identifying hazards, implementing safety measures, and providing adequate training, employers can mitigate the risks associated with arc flashes and create a safer work environment for everyone.
Compliance with OSHA regulations regarding arc flash risk assessments is not just a legal obligation but a moral necessity. Prioritizing electrical safety not only saves lives and prevents injuries but also preserves the integrity of equipment and facilities, ultimately contributing to the overall success and sustainability of businesses.