Am I Required to Have an Arc Flash Study? Understanding the Necessity and Benefits
In industrial and commercial settings where electrical systems are a critical part of daily operations, safety is paramount. One essential element of electrical safety is the arc flash study. But what exactly is an arc flash study, and are you required to have one performed? In this article, we’ll explore the importance of arc flash studies, when they are necessary, and the regulatory requirements surrounding them.
What is an Arc Flash?
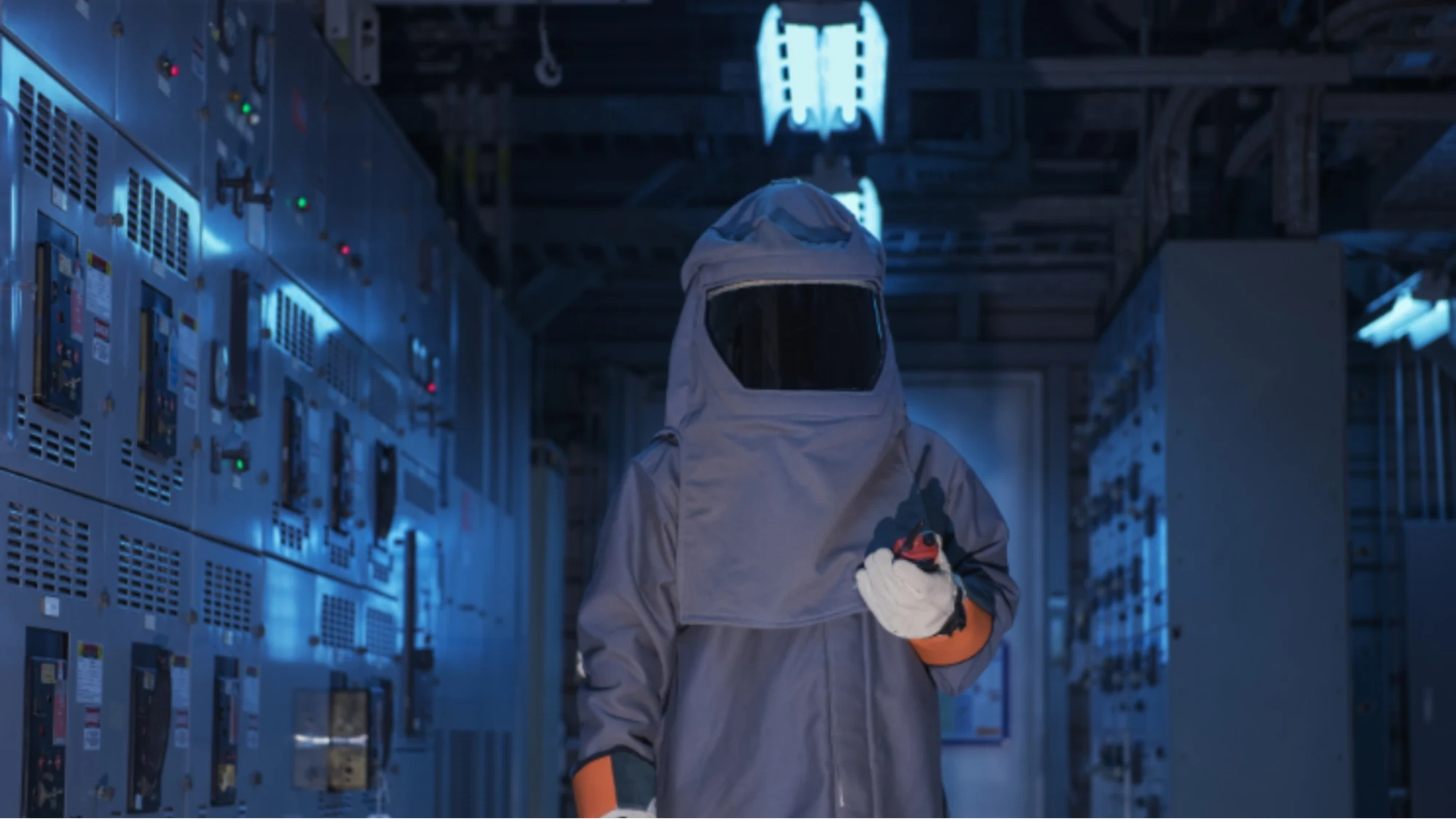
Before diving into the requirements for an arc flash study, it’s important to understand what an arc flash is. An arc flash is a dangerous and often catastrophic electrical explosion caused by a fault in an electrical system. When an arc flash occurs, it can result in severe injuries or fatalities, not only to workers but also to anyone near the equipment. These incidents release a massive amount of energy in the form of heat, light, and pressure, causing severe burns, hearing damage, and even vaporizing metal components in the system.
What is an Arc Flash Study?
An arc flash study, also known as an arc flash risk assessment, is an in-depth analysis of a facility’s electrical distribution system to identify potential arc flash hazards. The study evaluates how electrical energy would behave during a fault, estimates the potential incident energy that could be released, and determines what personal protective equipment (PPE) would be required to keep workers safe. The results of an arc flash study are used to label equipment with appropriate hazard levels and required PPE, ensuring compliance with safety standards and reducing the risk of arc flash incidents.
Are You Required to Have an Arc Flash Study?
The need for an arc flash study is governed by a combination of OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) regulations and the NFPA 70E standard for electrical safety in the workplace. Let’s break down how these regulations apply:
- OSHA Requirements
While OSHA does not explicitly mandate an arc flash study, it does require that employers protect workers from electrical hazards. OSHA’s regulations, specifically 29 CFR 1910.333(a), state that employers must assess electrical hazards and implement safe work practices. This includes identifying risks such as arc flash hazards and ensuring workers have proper PPE and training.
To comply with OSHA’s requirements for electrical safety, most employers turn to the NFPA 70E standard, which provides a detailed framework for identifying and mitigating electrical hazards, including arc flash risks. In essence, while OSHA doesn’t directly mention arc flash studies, failing to conduct one would likely result in non-compliance with OSHA’s overarching electrical safety standards.
- NFPA 70E Requirements
The NFPA 70E standard outlines the necessary steps for conducting an arc flash risk assessment. According to NFPA 70E, an arc flash study is required whenever electrical work is performed in environments where the potential for arc flash hazards exists. The standard specifies that an arc flash risk assessment must be conducted:
- Before any worker interacts with electrical equipment where energized parts are exposed or where work is being performed near energized parts.
- When equipment is new or if there are significant changes to the electrical system.
- Periodically reassessed to ensure the study remains accurate, especially when modifications or upgrades are made to the electrical system.
The goal of the NFPA 70E standard is to protect workers by ensuring that electrical hazards are properly evaluated, and that appropriate safety measures (such as PPE and labeling) are in place.
- NEC and IEEE Standards
In addition to NFPA 70E, the National Electrical Code (NEC) and IEEE 1584 guidelines also provide recommendations for conducting arc flash studies. While the NEC focuses on electrical installations and design, it references the importance of assessing arc flash hazards, particularly in high-energy systems. IEEE 1584 offers technical methods used to calculate potential incident energy during an arc flash event, which is a key component of an arc flash study.
When is an Arc Flash Study Not Required?
While the vast majority of industrial and commercial electrical systems require an arc flash study, there are a few exceptions:
- Low-voltage equipment (typically below 240V) may not always require an arc flash study, particularly if the fault current is below a certain threshold. However, this should be verified through a risk assessment.
- Infrequent interaction with electrical systems: If electrical work is rarely performed or if the system can always be fully de-energized before work is done, an arc flash study may not be necessary. However, these situations are rare in most active facilities.
Even in these cases, it’s crucial to ensure that workers are adequately protected, and that all applicable OSHA and NFPA 70E safety measures are followed.
What Happens During an Arc Flash Study?
An arc flash study typically follows these key steps:
- Data Collection: Engineers will gather information about the facility’s electrical system, including the equipment’s configuration, voltage levels, and fault current levels.
- System Modeling: Using software tools, the electrical system is modeled to simulate different fault conditions. This helps engineers understand the energy that could be released in an arc flash event.
- Incident Energy Analysis: The study calculates the potential incident energy levels at various points in the system. This information is used to determine the arc flash boundary—the distance within which workers would be at risk of injury during an arc flash.
- PPE Recommendations: Based on the calculated incident energy, the study specifies the level of PPE required to protect workers from arc flash hazards.
- Labeling and Documentation: Electrical equipment is labeled with the appropriate arc flash hazard levels and PPE requirements. The study results are documented for ongoing reference and compliance.
Benefits of an Arc Flash Study
Beyond regulatory compliance, there are several benefits to conducting an arc flash study:
- Worker Safety: The primary goal of an arc flash study is to protect workers by identifying hazards and ensuring they have the right PPE to minimize injury in case of an arc flash incident.
- Regulatory Compliance: Conducting an arc flash study helps ensure compliance with OSHA, NFPA 70E, NEC, and IEEE standards, avoiding costly fines and penalties.
- Improved System Reliability: An arc flash study often uncovers areas where the electrical system could be improved for better reliability and performance, reducing the risk of downtime.
- Liability Reduction: In the event of an incident, having an arc flash study in place demonstrates due diligence in providing a safe working environment, potentially reducing legal and financial liability.
Do You Need an Arc Flash Study? Our Recommendation
In most industrial and commercial settings, an arc flash study is not only recommended but required to ensure worker safety and regulatory compliance. If your facility has electrical equipment where energized work is performed, or if there have been significant changes to your system, an arc flash study should be carried out as soon as possible. By conducting this study, you are not only protecting your workers but also safeguarding your business from potential hazards and ensuring compliance with national safety standards.
If you’re unsure whether your facility needs an arc flash study, it’s always best to consult with a qualified electrical consultant who can evaluate your system and recommend the appropriate steps to enhance safety and compliance.
To learn more about arc flash studies and ensure your facility is up to code, reach out to the professional team at Shaw Consulting Services. Our experts are here to help you navigate electrical safety requirements and protect your team. Call us today at (470) 641-2562 or visit our website at shawengr.com.